Difference between revisions of "HAEM5:Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma"
Templates/files updated (unreviewed pages in bold): HAEM5:Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
| [checked revision] | [pending revision] |
Bailey.Glen (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma}} | ||
| − | |||
[[HAEM5:Table_of_Contents|Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | [[HAEM5:Table_of_Contents|Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 7: | ||
Amanda Xu, MD, Queen's University | Amanda Xu, MD, Queen's University | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==WHO Classification of Disease== | ==WHO Classification of Disease== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 26: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Subtype(s) | |Subtype(s) | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | |} | ||
| + | ==WHO Essential and Desirable Genetic Diagnostic Criteria== | ||
| + | <span style="color:#0070C0">(''Instructions: The table will have the diagnostic criteria from the WHO book <u>autocompleted</u>; remove any <u>non</u>-genetics related criteria. If applicable, add text about other classification'' ''systems that define this entity and specify how the genetics-related criteria differ.'')</span> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ | ||
| + | |WHO Essential Criteria (Genetics)* | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |WHO Desirable Criteria (Genetics)* | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Other Classification | ||
| + | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Note: These are only the genetic/genomic criteria. Additional diagnostic criteria can be found in the [https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/home <u>WHO Classification of Tumours</u>]. | |
| − | + | ==Related Terminology== | |
| − | + | <span style="color:#0070C0">(''Instructions: The table will have the related terminology from the WHO <u>autocompleted</u>.)''</span> | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | | | + | |+ |
| − | | | + | |Acceptable |
| − | + | | | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Not Recommended | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ==Gene Rearrangements== | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | !Driver Gene!!Fusion(s) and Common Partner Genes!!Molecular Pathogenesis!!Typical Chromosomal Alteration(s) | ||
| + | !Prevalence -Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | ||
| + | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
| + | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
| + | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | + | | | |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !Chr #!!'''Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH'''!!'''Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size]'''!!'''Relevant Gene(s)''' |
| + | !'''Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T''' | ||
| + | !'''Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source)''' | ||
| + | !'''Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> |
| + | 7 | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Loss | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | chr7 | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Unknown | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> D, P | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> No | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Presence of monosomy 7 (or 7q deletion) is sufficient for a diagnosis of AML with MDS-related changes when there is ≥20% blasts and no prior therapy (add reference). Monosomy 7/7q deletion is associated with a poor prognosis in AML (add references). | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> |
| − | | | + | 8 |
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Gain | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | chr8 | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Unknown | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> D, P | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Common recurrent secondary finding for t(8;21) (add references). | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> |
| + | 17 | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Amp | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | 17q12; chr17:39,700,064-39,728,658 [hg38; 28.6 kb] | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | ''ERBB2'' | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> D, P, T | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Amplification of ''ERBB2'' is associated with HER2 overexpression in HER2 positive breast cancer (add references). Add criteria for how amplification is defined. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 149: | Line 144: | ||
Other less common chromosomal alterations include gain of 1p, 2q, 6p, 10q, 11q, 12q, 13q, 17q, 19p, 20q, and Xp; and loss of 1p36, 2p16, 4q12, 4q31-32, 5p14, 5q34-35, 6q13-14, 6q16-27, 11q22-23, 12q, 13q12-14, 13q14-34, 17p13, and entire chromosome X<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Nakashima|first=Yasuhiro|last2=Tagawa|first2=Hiroyuki|last3=Suzuki|first3=Ritsuro|last4=Karnan|first4=Sivasundaram|last5=Karube|first5=Kennosuke|last6=Ohshima|first6=Koichi|last7=Muta|first7=Koichiro|last8=Nawata|first8=Hajime|last9=Morishima|first9=Yasuo|date=2005-11|title=Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia: different genomic alteration patterns of aggressive NK-cell leukemia and extranodal Nk/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16049916|journal=Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer|volume=44|issue=3|pages=247–255|doi=10.1002/gcc.20245|issn=1045-2257|pmid=16049916}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Siu|first=L. L.|last2=Chan|first2=V.|last3=Chan|first3=J. K.|last4=Wong|first4=K. F.|last5=Liang|first5=R.|last6=Kwong|first6=Y. L.|date=2000-12|title=Consistent patterns of allelic loss in natural killer cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11106552|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=157|issue=6|pages=1803–1809|doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64818-3|issn=0002-9440|pmc=1885756|pmid=11106552}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Siu|first=L. L.|last2=Wong|first2=K. F.|last3=Chan|first3=J. K.|last4=Kwong|first4=Y. L.|date=1999-11|title=Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia. Recognition of consistent patterns of genetic alterations|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10550295|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=155|issue=5|pages=1419–1425|doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65454-5|issn=0002-9440|pmc=1866965|pmid=10550295}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wong|first=K. F.|last2=Zhang|first2=Y. M.|last3=Chan|first3=J. K.|date=1999-07|title=Cytogenetic abnormalities in natural killer cell lymphoma/leukaemia--is there a consistent pattern?|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10439361|journal=Leukemia & Lymphoma|volume=34|issue=3-4|pages=241–250|doi=10.3109/10428199909050949|issn=1042-8194|pmid=10439361}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Ko|first=Y. H.|last2=Choi|first2=K. E.|last3=Han|first3=J. H.|last4=Kim|first4=J. M.|last5=Ree|first5=H. J.|date=2001-04-15|title=Comparative genomic hybridization study of nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11309817|journal=Cytometry|volume=46|issue=2|pages=85–91|doi=10.1002/cyto.1069|issn=0196-4763|pmid=11309817}}</ref>. | Other less common chromosomal alterations include gain of 1p, 2q, 6p, 10q, 11q, 12q, 13q, 17q, 19p, 20q, and Xp; and loss of 1p36, 2p16, 4q12, 4q31-32, 5p14, 5q34-35, 6q13-14, 6q16-27, 11q22-23, 12q, 13q12-14, 13q14-34, 17p13, and entire chromosome X<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Nakashima|first=Yasuhiro|last2=Tagawa|first2=Hiroyuki|last3=Suzuki|first3=Ritsuro|last4=Karnan|first4=Sivasundaram|last5=Karube|first5=Kennosuke|last6=Ohshima|first6=Koichi|last7=Muta|first7=Koichiro|last8=Nawata|first8=Hajime|last9=Morishima|first9=Yasuo|date=2005-11|title=Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia: different genomic alteration patterns of aggressive NK-cell leukemia and extranodal Nk/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16049916|journal=Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer|volume=44|issue=3|pages=247–255|doi=10.1002/gcc.20245|issn=1045-2257|pmid=16049916}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Siu|first=L. L.|last2=Chan|first2=V.|last3=Chan|first3=J. K.|last4=Wong|first4=K. F.|last5=Liang|first5=R.|last6=Kwong|first6=Y. L.|date=2000-12|title=Consistent patterns of allelic loss in natural killer cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11106552|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=157|issue=6|pages=1803–1809|doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64818-3|issn=0002-9440|pmc=1885756|pmid=11106552}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Siu|first=L. L.|last2=Wong|first2=K. F.|last3=Chan|first3=J. K.|last4=Kwong|first4=Y. L.|date=1999-11|title=Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia. Recognition of consistent patterns of genetic alterations|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10550295|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=155|issue=5|pages=1419–1425|doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65454-5|issn=0002-9440|pmc=1866965|pmid=10550295}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wong|first=K. F.|last2=Zhang|first2=Y. M.|last3=Chan|first3=J. K.|date=1999-07|title=Cytogenetic abnormalities in natural killer cell lymphoma/leukaemia--is there a consistent pattern?|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10439361|journal=Leukemia & Lymphoma|volume=34|issue=3-4|pages=241–250|doi=10.3109/10428199909050949|issn=1042-8194|pmid=10439361}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Ko|first=Y. H.|last2=Choi|first2=K. E.|last3=Han|first3=J. H.|last4=Kim|first4=J. M.|last5=Ree|first5=H. J.|date=2001-04-15|title=Comparative genomic hybridization study of nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11309817|journal=Cytometry|volume=46|issue=2|pages=85–91|doi=10.1002/cyto.1069|issn=0196-4763|pmid=11309817}}</ref>. | ||
| − | ==Characteristic Chromosomal Patterns== | + | ==Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns== |
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Chromosomal Pattern | ||
| + | !Molecular Pathogenesis | ||
| + | !'''Prevalence -''' | ||
| + | '''Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease)''' | ||
| + | !'''Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T''' | ||
| + | !'''Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source)''' | ||
| + | !'''Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Co-deletion of 1p and 18q | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> See chromosomal rearrangements table as this pattern is due to an unbalanced derivative translocation associated with oligodendroglioma (add reference). | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Common (Oligodendroglioma) | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> D, P | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| + | Microsatellite instability - hypermutated | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Common (Endometrial carcinoma) | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> P, T | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 171: | Line 199: | ||
|N/A | |N/A | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| + | ==Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Gene!!'''Genetic Alteration'''!!'''Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other'''!!'''Prevalence -''' | ||
| + | '''Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease)''' | ||
| + | !'''Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T ''' | ||
| + | !'''Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source)''' | ||
| + | !'''Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span>''EGFR'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Exon 18-21 activating mutations | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Oncogene | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Common (lung cancer) | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> T | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Yes (NCCN) | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Exons 18, 19, and 21 mutations are targetable for therapy. Exon 20 T790M variants cause resistance to first generation TKI therapy and are targetable by second and third generation TKIs (add references). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> ''TP53''; Variable LOF mutations | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Variable LOF mutations | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Tumor Supressor Gene | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Common (breast cancer) | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> P | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> >90% are somatic; rare germline alterations associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (add reference). Denotes a poor prognosis in breast cancer. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> ''BRAF''; Activating mutations | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Activating mutations | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Oncogene | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Common (melanoma) | ||
| + | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> T | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 186: | Line 257: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
|Pan-JAK and selective JAK3 inhibitors have been suggested as potential therapeutic options<ref name=":10" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Nairismägi|first=M.-L.|last2=Gerritsen|first2=M. E.|last3=Li|first3=Z. M.|last4=Wijaya|first4=G. C.|last5=Chia|first5=B. K. H.|last6=Laurensia|first6=Y.|last7=Lim|first7=J. Q.|last8=Yeoh|first8=K. W.|last9=Yao|first9=X. S.|date=2018-05|title=Oncogenic activation of JAK3-STAT signaling confers clinical sensitivity to PRN371, a novel selective and potent JAK3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29434279|journal=Leukemia|volume=32|issue=5|pages=1147–1156|doi=10.1038/s41375-017-0004-x|issn=1476-5551|pmc=5940653|pmid=29434279}}</ref>. [https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02974647 Clinical trials evaluating JAK inhibitors] are in progress. | |Pan-JAK and selective JAK3 inhibitors have been suggested as potential therapeutic options<ref name=":10" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Nairismägi|first=M.-L.|last2=Gerritsen|first2=M. E.|last3=Li|first3=Z. M.|last4=Wijaya|first4=G. C.|last5=Chia|first5=B. K. H.|last6=Laurensia|first6=Y.|last7=Lim|first7=J. Q.|last8=Yeoh|first8=K. W.|last9=Yao|first9=X. S.|date=2018-05|title=Oncogenic activation of JAK3-STAT signaling confers clinical sensitivity to PRN371, a novel selective and potent JAK3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29434279|journal=Leukemia|volume=32|issue=5|pages=1147–1156|doi=10.1038/s41375-017-0004-x|issn=1476-5551|pmc=5940653|pmid=29434279}}</ref>. [https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02974647 Clinical trials evaluating JAK inhibitors] are in progress. | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 193: | Line 264: | ||
|''STAT3''<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Jiang|first=Lu|last2=Gu|first2=Zhao-Hui|last3=Yan|first3=Zi-Xun|last4=Zhao|first4=Xia|last5=Xie|first5=Yin-Yin|last6=Zhang|first6=Zi-Guan|last7=Pan|first7=Chun-Ming|last8=Hu|first8=Yuan|last9=Cai|first9=Chang-Ping|date=2015-09|title=Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26192917|journal=Nature Genetics|volume=47|issue=9|pages=1061–1066|doi=10.1038/ng.3358|issn=1546-1718|pmid=26192917}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{Cite journal|last=Küçük|first=Can|last2=Jiang|first2=Bei|last3=Hu|first3=Xiaozhou|last4=Zhang|first4=Wenyan|last5=Chan|first5=John K. C.|last6=Xiao|first6=Wenming|last7=Lack|first7=Nathan|last8=Alkan|first8=Can|last9=Williams|first9=John C.|date=2015-01-14|title=Activating mutations of STAT5B and STAT3 in lymphomas derived from γδ-T or NK cells|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25586472|journal=Nature Communications|volume=6|pages=6025|doi=10.1038/ncomms7025|issn=2041-1723|pmc=7743911|pmid=25586472}}</ref><ref name=":4">{{Cite journal|last=Lee|first=Seungbok|last2=Park|first2=Ha Young|last3=Kang|first3=So Young|last4=Kim|first4=Seok Jin|last5=Hwang|first5=Jinha|last6=Lee|first6=Seungho|last7=Kwak|first7=Soo Heon|last8=Park|first8=Kyong Soo|last9=Yoo|first9=Hae Yong|date=2015-07-10|title=Genetic alterations of JAK/STAT cascade and histone modification in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25980440|journal=Oncotarget|volume=6|issue=19|pages=17764–17776|doi=10.18632/oncotarget.3776|issn=1949-2553|pmc=4627344|pmid=25980440}}</ref> | |''STAT3''<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Jiang|first=Lu|last2=Gu|first2=Zhao-Hui|last3=Yan|first3=Zi-Xun|last4=Zhao|first4=Xia|last5=Xie|first5=Yin-Yin|last6=Zhang|first6=Zi-Guan|last7=Pan|first7=Chun-Ming|last8=Hu|first8=Yuan|last9=Cai|first9=Chang-Ping|date=2015-09|title=Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26192917|journal=Nature Genetics|volume=47|issue=9|pages=1061–1066|doi=10.1038/ng.3358|issn=1546-1718|pmid=26192917}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{Cite journal|last=Küçük|first=Can|last2=Jiang|first2=Bei|last3=Hu|first3=Xiaozhou|last4=Zhang|first4=Wenyan|last5=Chan|first5=John K. C.|last6=Xiao|first6=Wenming|last7=Lack|first7=Nathan|last8=Alkan|first8=Can|last9=Williams|first9=John C.|date=2015-01-14|title=Activating mutations of STAT5B and STAT3 in lymphomas derived from γδ-T or NK cells|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25586472|journal=Nature Communications|volume=6|pages=6025|doi=10.1038/ncomms7025|issn=2041-1723|pmc=7743911|pmid=25586472}}</ref><ref name=":4">{{Cite journal|last=Lee|first=Seungbok|last2=Park|first2=Ha Young|last3=Kang|first3=So Young|last4=Kim|first4=Seok Jin|last5=Hwang|first5=Jinha|last6=Lee|first6=Seungho|last7=Kwak|first7=Soo Heon|last8=Park|first8=Kyong Soo|last9=Yoo|first9=Hae Yong|date=2015-07-10|title=Genetic alterations of JAK/STAT cascade and histone modification in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25980440|journal=Oncotarget|volume=6|issue=19|pages=17764–17776|doi=10.18632/oncotarget.3776|issn=1949-2553|pmc=4627344|pmid=25980440}}</ref> | ||
|Oncogene | |Oncogene | ||
| − | |26%<ref name=":4" /> | + | |6-26%<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":4" /> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
|STAT3 inhibitor may have potential therapeutic benefit in patients with STAT3 activating mutation<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wang|first=Yali|last2=Zhou|first2=Wenbo|last3=Chen|first3=Jianfeng|last4=Chen|first4=Jinghong|last5=Deng|first5=Peng|last6=Chen|first6=Huang|last7=Sun|first7=Yichen|last8=Yu|first8=Zhaoliang|last9=Pang|first9=Diwen|date=2023-08|title=Preclinical characterization of WB737, a potent and selective STAT3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37334274|journal=MedComm|volume=4|issue=4|pages=e284|doi=10.1002/mco2.284|issn=2688-2663|pmc=PMC10274570|pmid=37334274}}</ref>. | |STAT3 inhibitor may have potential therapeutic benefit in patients with STAT3 activating mutation<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wang|first=Yali|last2=Zhou|first2=Wenbo|last3=Chen|first3=Jianfeng|last4=Chen|first4=Jinghong|last5=Deng|first5=Peng|last6=Chen|first6=Huang|last7=Sun|first7=Yichen|last8=Yu|first8=Zhaoliang|last9=Pang|first9=Diwen|date=2023-08|title=Preclinical characterization of WB737, a potent and selective STAT3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37334274|journal=MedComm|volume=4|issue=4|pages=e284|doi=10.1002/mco2.284|issn=2688-2663|pmc=PMC10274570|pmid=37334274}}</ref>. | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 203: | Line 274: | ||
|''STAT5B''<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":3" /> | |''STAT5B''<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":3" /> | ||
|Oncogene | |Oncogene | ||
| + | |6%<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 216: | Line 287: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 226: | Line 297: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''PDGFRA''<ref name=":13" /> |
| + | |Oncogene | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''EZH2''<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Yan|first=Junli|last2=Li|first2=Boheng|last3=Lin|first3=Baohong|last4=Lee|first4=Pei Tsung|last5=Chung|first5=Tae-Hoon|last6=Tan|first6=Joy|last7=Bi|first7=Chonglei|last8=Lee|first8=Xue Ting|last9=Selvarajan|first9=Viknesvaran|date=2016-08-18|title=EZH2 phosphorylation by JAK3 mediates a switch to noncanonical function in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27297789|journal=Blood|volume=128|issue=7|pages=948–958|doi=10.1182/blood-2016-01-690701|issn=1528-0020|pmid=27297789}}</ref> | ||
| + | |Oncogene | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''RAS/KRAS/HRAS'' |
|Oncogene | |Oncogene | ||
| + | |<5%<ref name=":14">{{Cite journal|last=Hoshida|first=Yoshihiko|last2=Hongyo|first2=Tadashi|last3=Jia|first3=Xinshan|last4=He|first4=Yanjiao|last5=Hasui|first5=Kazuhisa|last6=Dong|first6=Zhiming|last7=Luo|first7=Wen-Juan|last8=Ham|first8=Maria Francisca|last9=Nomura|first9=Taisei|date=2003-03|title=Analysis of p53, K-ras, c-kit, and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T cell lymphoma in northeast district of China|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12824925|journal=Cancer Science|volume=94|issue=3|pages=297–301|doi=10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01436.x|issn=1347-9032|pmc=PMC11160272|pmid=12824925}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Takahara|first=Miki|last2=Kishibe|first2=Kan|last3=Bandoh|first3=Nobuyuki|last4=Nonaka|first4=Satoshi|last5=Harabuchi|first5=Yasuaki|date=2004-01|title=P53, N- and K-Ras, and beta-catenin gene mutations and prognostic factors in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma from Hokkaido, Japan|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14745729|journal=Human Pathology|volume=35|issue=1|pages=86–95|doi=10.1016/j.humpath.2003.08.025|issn=0046-8177|pmid=14745729}}</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''FAS'' | ||
| + | |Oncogene | ||
| + | |50-60%<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Shen|first=Lijun|last2=Liang|first2=Anthony C. T.|last3=Lu|first3=Liwei|last4=Au|first4=Wing Yan|last5=Kwong|first5=Yok-Lam|last6=Liang|first6=Raymond H. S.|last7=Srivastava|first7=Gopesh|date=2002-12|title=Frequent deletion of Fas gene sequences encoding death and transmembrane domains in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12466128|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=161|issue=6|pages=2123–2131|doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64490-2|issn=0002-9440|pmc=1850920|pmid=12466128}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Takakuwa|first=Tetsuya|last2=Dong|first2=Zhiming|last3=Nakatsuka|first3=Shinichi|last4=Kojya|first4=Shizuo|last5=Harabuchi|first5=Yasuaki|last6=Yang|first6=Woo-Ick|last7=Nagata|first7=Shigekazu|last8=Aozasa|first8=Katsuyuki|date=2002-07-11|title=Frequent mutations of Fas gene in nasal NK/T cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12096347|journal=Oncogene|volume=21|issue=30|pages=4702–4705|doi=10.1038/sj.onc.1205571|issn=0950-9232|pmid=12096347}}</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''KIT'' |
|Oncogene | |Oncogene | ||
| + | |5-71% (China) | ||
| + | 22% (Japan)<ref name=":14" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Hongyo|first=T.|last2=Li|first2=T.|last3=Syaifudin|first3=M.|last4=Baskar|first4=R.|last5=Ikeda|first5=H.|last6=Kanakura|first6=Y.|last7=Aozasa|first7=K.|last8=Nomura|first8=T.|date=2000-05-01|title=Specific c-kit mutations in sinonasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma in China and Japan|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10811105|journal=Cancer Research|volume=60|issue=9|pages=2345–2347|issn=0008-5472|pmid=10811105}}</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''CTNNB1'' | ||
| + | |Oncogene | ||
| + | |16-30%<ref name=":14" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Sugimoto|first=Kei-ji|last2=Kawamata|first2=Norihiko|last3=Sakajiri|first3=Sakura|last4=Oshimi|first4=Kazuo|date=2002-11|title=Molecular analysis of oncogenes, ras family genes (N-ras, K-ras, H-ras), myc family genes (c-myc, N-myc) and mdm2 in natural killer cell neoplasms|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12460470|journal=Japanese Journal of Cancer Research: Gann|volume=93|issue=11|pages=1270–1277|doi=10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01234.x|issn=0910-5050|pmc=5926889|pmid=12460470}}</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''DDX3X''<ref name=":2" /> | |''DDX3X''<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| − | | | + | |Epigenetic modifier (RNA helicase) |
|20%<ref name=":2" /> | |20%<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''KMT2D (MLL2)''<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |Epigenetic modifier | ||
| + | |38.2%<ref name=":4" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''ARID1A''<ref name=":2" /> |
| − | | | + | |Epigenetic modifier |
| − | | | + | | |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''EP300''<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |Epigenetic modifier | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''ASXL3''<ref name=":2" /> |
| − | | | + | |Epigenetic modifier |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''BCOR''<ref name=":4" /> | ||
| + | |Epigenetic modifier | ||
| + | |38.2%<ref name=":4" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''TP53''<ref name=":2" /> |
|Tumor suppressor gene | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| + | |24-62%<ref name=":11">{{Cite journal|last=Quintanilla-Martinez|first=L.|last2=Kremer|first2=M.|last3=Keller|first3=G.|last4=Nathrath|first4=M.|last5=Gamboa-Dominguez|first5=A.|last6=Meneses|first6=A.|last7=Luna-Contreras|first7=L.|last8=Cabras|first8=A.|last9=Hoefler|first9=H.|date=2001-12|title=p53 Mutations in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma from Mexico: association with large cell morphology and advanced disease|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11733360|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=159|issue=6|pages=2095–2105|doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63061-1|issn=0002-9440|pmc=1850589|pmid=11733360}}</ref><ref name=":8">{{Cite journal|last=Hongyo|first=Tadashi|last2=Hoshida|first2=Yoshihiko|last3=Nakatsuka|first3=Shin-Ichi|last4=Syaifudin|first4=Mukh|last5=Kojya|first5=Shizuo|last6=Yang|first6=Woo-Ick|last7=Min|first7=Yoo-Hong|last8=Chan|first8=Heekyung|last9=Kim|first9=Chan Hwan|date=2005-02|title=p53, K-ras, c-kit and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T-cell lymphoma in Korea and Japan|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15643509|journal=Oncology Reports|volume=13|issue=2|pages=265–271|issn=1021-335X|pmid=15643509}}</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Yes, associated with advanced stage disease<ref name=":11" />. | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''RUNX3''<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Selvarajan|first=V.|last2=Osato|first2=M.|last3=Nah|first3=G. S. S.|last4=Yan|first4=J.|last5=Chung|first5=T.-H.|last6=Voon|first6=D. C.-C.|last7=Ito|first7=Y.|last8=Ham|first8=M. F.|last9=Salto-Tellez|first9=M.|date=2017-10|title=RUNX3 is oncogenic in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and is transcriptionally regulated by MYC|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28119527|journal=Leukemia|volume=31|issue=10|pages=2219–2227|doi=10.1038/leu.2017.40|issn=1476-5551|pmc=5629367|pmid=28119527}}</ref> | ||
| + | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''MGA''<ref name=":2" /> |
|Tumor suppressor gene | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''PRDM1''<ref name=":9">{{Cite journal|last=Huang|first=Yenlin|last2=de Leval|first2=Laurence|last3=Gaulard|first3=Philippe|date=2013-03|title=Molecular underpinning of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23768641|journal=Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology|volume=26|issue=1|pages=57–74|doi=10.1016/j.beha.2013.04.006|issn=1532-1924|pmid=23768641}}</ref><ref name=":7" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Küçük|first=Can|last2=Iqbal|first2=Javeed|last3=Hu|first3=Xiaozhou|last4=Gaulard|first4=Phillip|last5=De Leval|first5=Laurence|last6=Srivastava|first6=Gopesh|last7=Au|first7=Wing Yan|last8=McKeithan|first8=Timothy W.|last9=Chan|first9=Wing C.|date=2011-12-13|title=PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in natural killer cell malignancies|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22143801|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America|volume=108|issue=50|pages=20119–20124|doi=10.1073/pnas.1115128108|issn=1091-6490|pmc=3250125|pmid=22143801}}</ref> | ||
| + | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| + | |Methylated in NK-92, KHYG-1, SNK-1, SNK-6 cell lines, 12/17 cases; Deleted in 8/18 cases; Mutated in NK-92 and KAI3 cell lines, 1/26 cases<ref name=":9" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''ATG5''<ref name=":9" /> |
|Tumor suppressor gene | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |''AIM1''<ref name=":9" /> | ||
| + | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| + | |Methylated in NK-92, HANK1, NK-YS, SNK-1, YT cell lines; Mutated in in SNK-1 and SNK-6 cell lines<ref name=":9" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| + | |Unknown | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''FOXO3''<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":7" /> | |''FOXO3''<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":7" /> | ||
|Tumor suppressor gene | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| + | |Mutated in 2/26 NKTCL and 1/9 ANKL<ref name=":9" /> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''HACE1''<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":13">{{Cite journal|last=Huang|first=Yenlin|last2=de Reyniès|first2=Aurélien|last3=de Leval|first3=Laurence|last4=Ghazi|first4=Bouchra|last5=Martin-Garcia|first5=Nadine|last6=Travert|first6=Marion|last7=Bosq|first7=Jacques|last8=Brière|first8=Josette|last9=Petit|first9=Barbara|date=2010-02-11|title=Gene expression profiling identifies emerging oncogenic pathways operating in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19965620|journal=Blood|volume=115|issue=6|pages=1226–1237|doi=10.1182/blood-2009-05-221275|issn=1528-0020|pmc=2826234|pmid=19965620}}</ref> | |''HACE1''<ref name=":9" /><ref name=":13">{{Cite journal|last=Huang|first=Yenlin|last2=de Reyniès|first2=Aurélien|last3=de Leval|first3=Laurence|last4=Ghazi|first4=Bouchra|last5=Martin-Garcia|first5=Nadine|last6=Travert|first6=Marion|last7=Bosq|first7=Jacques|last8=Brière|first8=Josette|last9=Petit|first9=Barbara|date=2010-02-11|title=Gene expression profiling identifies emerging oncogenic pathways operating in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19965620|journal=Blood|volume=115|issue=6|pages=1226–1237|doi=10.1182/blood-2009-05-221275|issn=1528-0020|pmc=2826234|pmid=19965620}}</ref> | ||
|Tumor suppressor gene | |Tumor suppressor gene | ||
| + | |Mutated in 6/9 (67%) cell lines and 5/15 (33%) primary tumors<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Küçük|first=Can|last2=Hu|first2=Xiaozhou|last3=Iqbal|first3=Javeed|last4=Gaulard|first4=Philippe|last5=Klinkebiel|first5=David|last6=Cornish|first6=Adam|last7=Dave|first7=Bhavana J.|last8=Chan|first8=Wing C.|date=2013-01|title=HACE1 is a tumor suppressor gene candidate in natural killer cell neoplasms|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23142381|journal=The American Journal of Pathology|volume=182|issue=1|pages=49–55|doi=10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.09.012|issn=1525-2191|pmc=3532710|pmid=23142381}}</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | | | + | |Unknown |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 350: | Line 512: | ||
==Genes and Main Pathways Involved== | ==Genes and Main Pathways Involved== | ||
| − | [https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/115/6/1226/26917/Gene-expression-profiling-identifies-emerging Huang, ''et al''] described deregulation of several signaling pathways in NK T-cell lymphoma, main ones listed below<ref name=":13" />. A review by [https://jhoonline.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13045-019-0716-7 De Mel, ''et al''], also outlines key molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of ENKTL<ref>{{Cite journal|last=de Mel|first=Sanjay|last2=Hue|first2=Susan Swee-Shan|last3=Jeyasekharan|first3=Anand D.|last4=Chng|first4=Wee-Joo|last5=Ng|first5=Siok-Bian|date=2019-04-02|title=Molecular pathogenic pathways in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30935402|journal=Journal of Hematology & Oncology|volume=12|issue=1|pages=33|doi=10.1186/s13045-019-0716-7|issn=1756-8722|pmc=6444858|pmid=30935402}}</ref>. | + | [https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/115/6/1226/26917/Gene-expression-profiling-identifies-emerging Huang, ''et al''] described deregulation of several signaling pathways in NK T-cell lymphoma, main ones listed below<ref name=":13" />. A review by [https://jhoonline.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13045-019-0716-7 De Mel, ''et al''], also outlines key molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of ENKTL<ref name=":15">{{Cite journal|last=de Mel|first=Sanjay|last2=Hue|first2=Susan Swee-Shan|last3=Jeyasekharan|first3=Anand D.|last4=Chng|first4=Wee-Joo|last5=Ng|first5=Siok-Bian|date=2019-04-02|title=Molecular pathogenic pathways in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30935402|journal=Journal of Hematology & Oncology|volume=12|issue=1|pages=33|doi=10.1186/s13045-019-0716-7|issn=1756-8722|pmc=6444858|pmid=30935402}}</ref>. |
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Gene; Genetic Alteration!!Pathway!!Pathophysiologic Outcome | !Gene; Genetic Alteration!!Pathway!!Pathophysiologic Outcome | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |''JAK3'', ''STAT3'', and ''STAT5B''; Activating mutations | + | |''JAK3'', ''STAT3'', and ''STAT5B''; Activating mutations<ref name=":13" /><ref name=":15" /> |
|JAK/STAT pathway | |JAK/STAT pathway | ||
|Increased cell growth and proliferation | |Increased cell growth and proliferation | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |''MYC, RUNX3'' | + | |''MYC, RUNX3''<ref name=":15" /> |
|MYC | |MYC | ||
|Increased cell proliferation and survival | |Increased cell proliferation and survival | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |''AKT'' and related genes | + | |''AKT'' and related genes<ref name=":13" /> |
|AKT pathway | |AKT pathway | ||
|Increased cell growth, proliferation and survival | |Increased cell growth, proliferation and survival | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |NF-κB related genes | + | |NF-κB related genes<ref name=":13" /><ref name=":15" /> |
|NF-κB pathway | |NF-κB pathway | ||
|Increased cell proliferation | |Increased cell proliferation | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |''PDGFRA'' | + | |''PDGFRA''<ref name=":13" /><ref name=":15" /> |
|PDGF pathway | |PDGF pathway | ||
|Increased cell proliferation and survival | |Increased cell proliferation and survival | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |''NOTCH1'' | + | |''NOTCH1''<ref name=":15" /> |
|NOTCH1 pathway | |NOTCH1 pathway | ||
|Increased cell proliferation | |Increased cell proliferation | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |AURKA | + | |AURKA<ref name=":15" /> |
|Aurora kinase pathway<ref name=":12" /> | |Aurora kinase pathway<ref name=":12" /> | ||
|Increased cell proliferation and cell cycle dysregulation | |Increased cell proliferation and cell cycle dysregulation | ||
| Line 393: | Line 555: | ||
==Additional Information== | ==Additional Information== | ||
| + | [[File:Extranodal NK T-cell lymphoma, nasal type.png|thumb|Extranodal NK T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (HPS). Angiocentric and angiodestructive growth pattern.]]This disease is <u>defined/characterized</u> as detailed below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lymphoma of NK or T-cell lineage strongly associated with Epstein-Barr virus<ref name=":6">{{Cite journal|last=Jaffe|first=E. S.|last2=Krenacs|first2=L.|last3=Kumar|first3=S.|last4=Kingma|first4=D. W.|last5=Raffeld|first5=M.|date=1999-01|title=Extranodal peripheral T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9894469|journal=American Journal of Clinical Pathology|volume=111|issue=1 Suppl 1|pages=S46–55|issn=0002-9173|pmid=9894469}}</ref>. The lineage (NK or T-cell) has no clinical significance<ref name=":16">{{Cite journal|last=Wang|first=Hua|last2=Fu|first2=Bi-Bo|last3=Gale|first3=Robert Peter|last4=Liang|first4=Yang|date=2021-09|title=NK-/T-cell lymphomas|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34117356|journal=Leukemia|volume=35|issue=9|pages=2460–2468|doi=10.1038/s41375-021-01313-2|issn=1476-5551|pmc=8410593|pmid=34117356}}</ref>. | ||
| + | *Divided into nasal and non-nasal types, the latter most often occurring in the skin and intestinal tract<ref name=":5">Chan J. K. C., et al., (2017). Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, in World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised 4th edition. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Arber DA, Hasserjian RP, Le Beau MM, Orazi A, and Siebert R, Editors. Revised 4th Edition. IARC Press: Lyon, France, p.368-371.</ref><ref name=":6" />. | ||
| + | *It is a destructive angiocentric disease characterized by vascular destruction and necrosis<ref name=":17">{{Cite journal|last=Aviles|first=A.|last2=Rodriguez|first2=L.|last3=Guzman|first3=R.|last4=Talavera|first4=A.|last5=Garcia|first5=E. L.|last6=Diaz-Maqueo|first6=J. C.|date=1992|title=Angiocentric T-cell lymphoma of the nose, paranasal sinuses and hard palate|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1398510|journal=Hematological Oncology|volume=10|issue=3-4|pages=141–147|doi=10.1002/hon.2900100303|issn=0278-0232|pmid=1398510}}</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Differential diagnosis: sinonasal carcinomas and other lymphomas of the nasal cavity, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma<ref name=":18">{{Cite journal|last=Steele|first=Toby O.|last2=Buniel|first2=Maria C.|last3=Mace|first3=Jess C.|last4=El Rassi|first4=Edward|last5=Smith|first5=Timothy L.|date=2016-09|title=Lymphoma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: A case series|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27657899|journal=American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy|volume=30|issue=5|pages=335–339|doi=10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4347|issn=1945-8932|pmid=27657899}}</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <u>epidemiology/prevalence</u> of this disease is detailed below: | ||
| − | N/A | + | *Most prevalent in East Asia and Latin America. |
| + | *Represents less than 1% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas in the United States | ||
| + | **Highest incidence among Asian Pacific Islanders and Hispanic populations<ref name=":19">{{Cite journal|last=Haverkos|first=Bradley M.|last2=Pan|first2=Zenggang|last3=Gru|first3=Alejandro A.|last4=Freud|first4=Aharon G.|last5=Rabinovitch|first5=Rachel|last6=Xu-Welliver|first6=Meng|last7=Otto|first7=Brad|last8=Barrionuevo|first8=Carlos|last9=Baiocchi|first9=Robert A.|date=2016-12|title=Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL-NT): An update on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and natural history in North American and European cases|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5199232/|journal=Current hematologic malignancy reports|volume=11|issue=6|pages=514–527|doi=10.1007/s11899-016-0355-9|issn=1558-8211|pmc=5199232|pmid=27778143}}</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <u>clinical features</u> of this disease are detailed below: [[File:Extranodal NK T-cell lymphoma, nasal type.vsi(17.8X) snapshot.png|thumb|Extranodal NK T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (HPS). Angiocentric and angiodestructive growth pattern.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Signs and symptoms - Nasal mass, nasal obstruction, nasal bleeding; Hoarseness, dysphagia, halitosis, airway obstruction, dysphonia; Abdominal pain, GI bleeding, bowel perforation<ref name=":0">Thida AM, Gohari P. Extranodal NK-Cell Lymphoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: <nowiki>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559207/</nowiki></ref>; B symptoms (fever, weight loss, night sweats) associated with higher clinical stage<ref name=":20">{{Cite journal|last=Takahara|first=Miki|last2=Kumai|first2=Takumi|last3=Kishibe|first3=Kan|last4=Nagato|first4=Toshihiro|last5=Harabuchi|first5=Yasuaki|date=2021-06-25|title=Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein-Barr Virus Relation|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34202088|journal=Microorganisms|volume=9|issue=7|pages=1381|doi=10.3390/microorganisms9071381|issn=2076-2607|pmc=8304202|pmid=34202088}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Laboratory findings - No specific findings; Cytopenias | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <u>sites of involvement</u> of this disease are detailed below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Most are nasal type involving the upper aerodigestive tract | ||
| + | *Extranasal type may involve skin, testis, and gastrointestinal tract<ref name=":0" />. | ||
| + | *Bone marrow involvement is uncommon<ref name=":21">{{Cite journal|last=Wong|first=K. F.|last2=Chan|first2=J. K.|last3=Cheung|first3=M. M.|last4=So|first4=J. C.|date=2001-02|title=Bone marrow involvement by nasal NK cell lymphoma at diagnosis is uncommon|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11211616|journal=American Journal of Clinical Pathology|volume=115|issue=2|pages=266–270|doi=10.1309/E5PR-6A9R-Q02N-8QVW|issn=0002-9173|pmid=11211616}}</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <u>morphologic features</u> of this disease are detailed below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Diffuse infiltrate composed of admixture of small, medium, or large and anaplastic cells. | ||
| + | *Cells have irregularly folded nuclei and moderate pale cytoplasm. | ||
| + | *Loss of mucosal glands. | ||
| + | *Angiocentric and angiodestructive growth pattern with coagulative necrosis. | ||
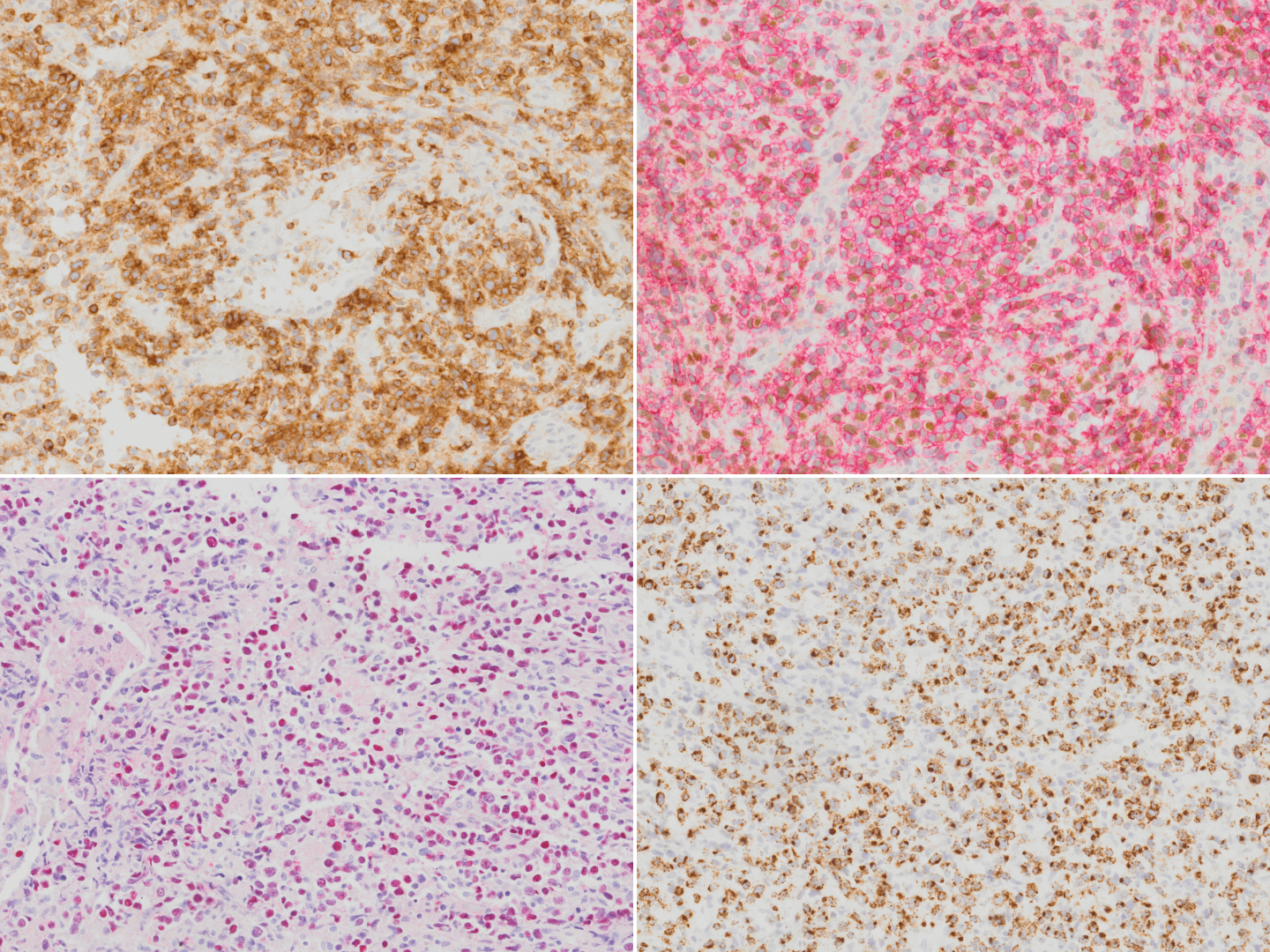
| + | *Usually see apoptotic cells and mitotic figures[[File:IHC NKTCL.png|thumb|Extranodal NK T-cell lymphoma stained with CD2 (top left), CD56 (red chromogen; top right), EBER in-situ hybridization (bottom left) and TIA1 (bottom right).]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The pitfalls can include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Mucosal ulceration and superimposed inflammation can mimic an inflammatory process, particularly in less aggressive cases<ref name=":22">Devins, K., Schuster, S.J., Caponetti, G.C. ''et al.'' Rare case of low-grade extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, arising in the setting of chronic rhinosinusitis and harboring a novel N-terminal ''KIT'' mutation. ''Diagn Pathol'' 13, 92 (2018). <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-018-0765-1</nowiki></ref>. | ||
| + | *Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the overlying mucosal epithelium can mimic squamous cell carcinoma<ref name=":23">{{Cite journal|last=Ling|first=Yi-Hong|last2=Zhu|first2=Chong-Mei|last3=Wen|first3=Shi-Hong|last4=Luo|first4=Rong-Zhen|last5=Li|first5=Peng|last6=Cao|first6=Yun|last7=Rao|first7=Hui-Lan|last8=Lin|first8=Su-Xia|last9=Cai|first9=Mu-Yan|date=2015-09|title=Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia mimicking invasive squamous cell carcinoma in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a report of 34 cases|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25619876|journal=Histopathology|volume=67|issue=3|pages=404–409|doi=10.1111/his.12656|issn=1365-2559|pmid=25619876}}</ref><ref name=":24">{{Cite journal|last=Xiang|first=Chun-Xiang|last2=Chen|first2=Zi-Hang|last3=Zhao|first3=Sha|last4=Gao|first4=Li-Min|last5=Tao|first5=Qing|last6=Zuo|first6=Zhuo|last7=Liu|first7=Xiao-Yu|last8=Liu|first8=Wei-Ping|date=2019-07|title=Laryngeal Extranodal Nasal-type Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 31 Cases in China|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31045893|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=43|issue=7|pages=995–1004|doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000001266|issn=1532-0979|pmid=31045893}}</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <u>immunophenotype</u> of this disease is detailed below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Positive (universal) - EBER / EBV | ||
| + | |||
| + | Positive (majority) - cytoplasmic CD3ε, CD2, CD56, granzyme B, and TIA-1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Positive (subset) - TCR αβ/γδ, HLA-DR, CD25, pSTAT3, CXCL13, IRF4/MUM1, CD16, Fas, FasL, MATK, CD30<ref name=":25">{{Cite journal|last=Li|first=Shaoying|last2=Feng|first2=Xiaoli|last3=Li|first3=Ting|last4=Zhang|first4=Shuang|last5=Zuo|first5=Zhuang|last6=Lin|first6=Pei|last7=Konoplev|first7=Sergej|last8=Bueso-Ramos|first8=Carlos E.|last9=Vega|first9=Francisco|date=2013-01|title=Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a report of 73 cases at MD Anderson Cancer Center|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23232851|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=37|issue=1|pages=14–23|doi=10.1097/PAS.0b013e31826731b5|issn=1532-0979|pmid=23232851}}</ref><ref name=":26">{{Cite journal|last=Jhuang|first=Jie-Yang|last2=Chang|first2=Sheng-Tsung|last3=Weng|first3=Shih-Feng|last4=Pan|first4=Shien-Tung|last5=Chu|first5=Pei-Yi|last6=Hsieh|first6=Pin-Pen|last7=Wei|first7=Chih-Hsin|last8=Chou|first8=Shih-Cheng|last9=Koo|first9=Chiew-Loon|date=2015-02|title=Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type in Taiwan: a relatively higher frequency of T-cell lineage and poor survival for extranasal tumors|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25554090|journal=Human Pathology|volume=46|issue=2|pages=313–321|doi=10.1016/j.humpath.2014.11.008|issn=1532-8392|pmid=25554090}}</ref><ref name=":27">{{Cite journal|last=Pongpruttipan|first=Tawatchai|last2=Sukpanichnant|first2=Sanya|last3=Assanasen|first3=Thamathorn|last4=Wannakrairot|first4=Pongsak|last5=Boonsakan|first5=Paisarn|last6=Kanoksil|first6=Wasana|last7=Kayasut|first7=Kanita|last8=Mitarnun|first8=Winyou|last9=Khuhapinant|first9=Archrob|date=2012-04|title=Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, includes cases of natural killer cell and αβ, γδ, and αβ/γδ T-cell origin: a comprehensive clinicopathologic and phenotypic study|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22314189|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=36|issue=4|pages=481–499|doi=10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824433d8|issn=1532-0979|pmid=22314189}}</ref><ref name=":28">{{Cite journal|last=Jaffe|first=E. S.|last2=Chan|first2=J. K.|last3=Su|first3=I. J.|last4=Frizzera|first4=G.|last5=Mori|first5=S.|last6=Feller|first6=A. C.|last7=Ho|first7=F. C.|date=1996-01|title=Report of the Workshop on Nasal and Related Extranodal Angiocentric T/Natural Killer Cell Lymphomas. Definitions, differential diagnosis, and epidemiology|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8540601|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=20|issue=1|pages=103–111|doi=10.1097/00000478-199601000-00012|issn=0147-5185|pmid=8540601}}</ref><ref name=":29">{{Cite journal|last=Ohshima|first=K.|last2=Suzumiya|first2=J.|last3=Shimazaki|first3=K.|last4=Kato|first4=A.|last5=Tanaka|first5=T.|last6=Kanda|first6=M.|last7=Kikuchi|first7=M.|date=1997-11|title=Nasal T/NK cell lymphomas commonly express perforin and Fas ligand: important mediators of tissue damage|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9416485|journal=Histopathology|volume=31|issue=5|pages=444–450|doi=10.1046/j.1365-2559.1997.2880887.x|issn=0309-0167|pmid=9416485}}</ref><ref name=":30">{{Cite journal|last=Takata|first=Katsuyoshi|last2=Hong|first2=Min-Eui|last3=Sitthinamsuwan|first3=Panitta|last4=Loong|first4=Florence|last5=Tan|first5=Soo-Yong|last6=Liau|first6=Jau-Yu|last7=Hsieh|first7=Pin-Pen|last8=Ng|first8=Siok-Bian|last9=Yang|first9=Sheau-Fang|date=2015-01|title=Primary cutaneous NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type and CD56-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a cellular lineage and clinicopathologic study of 60 patients from Asia|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25188863|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=39|issue=1|pages=1–12|doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000000312|issn=1532-0979|pmid=25188863}}</ref><ref name=":31">{{Cite journal|last=Kuo|first=Tseng-Tong|last2=Shih|first2=Lee-Yung|last3=Tsang|first3=Ngan-Ming|date=2004-10|title=Nasal NK/T cell lymphoma in Taiwan: a clinicopathologic study of 22 cases, with analysis of histologic subtypes, Epstein-Barr virus LMP-1 gene association, and treatment modalities|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15494863|journal=International Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=12|issue=4|pages=375–387|doi=10.1177/106689690401200410|issn=1066-8969|pmid=15494863}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Negative (universal) - CD4, CD8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Negative (subset) - Surface CD3 (subset of T-cell lineage)<ref name=":0" /> | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| Line 404: | Line 614: | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| − | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Primary authors will typically be those that initially create and complete the content of a page. If a subsequent user modifies the content and feels the effort put forth is of high enough significance to warrant listing in the authorship section, please contact the CCGA | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Primary authors will typically be those that initially create and complete the content of a page. If a subsequent user modifies the content and feels the effort put forth is of high enough significance to warrant listing in the authorship section, please contact the [[Leadership|''<u>Associate Editor</u>'']] or other CCGA representative. When pages have a major update, the new author will be acknowledged at the beginning of the page, and those who contributed previously will be acknowledged below as a prior author. |
| + | |||
| + | Prior Author(s): | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<nowiki>*</nowiki>''Citation of this Page'': “Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated {{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}}, <nowiki>https://ccga.io/index.php/HAEM5:Extranodal_NK/T-cell_lymphoma</nowiki>. | <nowiki>*</nowiki>''Citation of this Page'': “Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated {{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}}, <nowiki>https://ccga.io/index.php/HAEM5:Extranodal_NK/T-cell_lymphoma</nowiki>. | ||
[[Category:HAEM5]] | [[Category:HAEM5]] | ||
[[Category:DISEASE]] | [[Category:DISEASE]] | ||
[[Category:Diseases E]] | [[Category:Diseases E]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:36, 24 March 2025
Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)
Primary Authors*
Teodora Popa, MD, Queen's University
Amanda Xu, MD, Queen's University
WHO Classification of Disease
| Structure | Disease |
|---|---|
| Book | Haematolymphoid Tumours (5th ed.) |
| Category | T-cell and NK-cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas |
| Family | Mature T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms |
| Type | EBV-positive NK-cell and T-cell lymphomas |
| Subtype(s) |
WHO Essential and Desirable Genetic Diagnostic Criteria
(Instructions: The table will have the diagnostic criteria from the WHO book autocompleted; remove any non-genetics related criteria. If applicable, add text about other classification systems that define this entity and specify how the genetics-related criteria differ.)
| WHO Essential Criteria (Genetics)* | |
| WHO Desirable Criteria (Genetics)* | |
| Other Classification |
*Note: These are only the genetic/genomic criteria. Additional diagnostic criteria can be found in the WHO Classification of Tumours.
Related Terminology
(Instructions: The table will have the related terminology from the WHO autocompleted.)
| Acceptable | |
| Not Recommended |
Gene Rearrangements
| Driver Gene | Fusion(s) and Common Partner Genes | Molecular Pathogenesis | Typical Chromosomal Alteration(s) | Prevalence -Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH
| Chr # | Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH | Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size] | Relevant Gene(s) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE:
7 |
EXAMPLE: Loss | EXAMPLE:
chr7 |
EXAMPLE:
Unknown |
EXAMPLE: D, P | EXAMPLE: No | EXAMPLE:
Presence of monosomy 7 (or 7q deletion) is sufficient for a diagnosis of AML with MDS-related changes when there is ≥20% blasts and no prior therapy (add reference). Monosomy 7/7q deletion is associated with a poor prognosis in AML (add references). |
| EXAMPLE:
8 |
EXAMPLE: Gain | EXAMPLE:
chr8 |
EXAMPLE:
Unknown |
EXAMPLE: D, P | EXAMPLE:
Common recurrent secondary finding for t(8;21) (add references). | |
| EXAMPLE:
17 |
EXAMPLE: Amp | EXAMPLE:
17q12; chr17:39,700,064-39,728,658 [hg38; 28.6 kb] |
EXAMPLE:
ERBB2 |
EXAMPLE: D, P, T | EXAMPLE:
Amplification of ERBB2 is associated with HER2 overexpression in HER2 positive breast cancer (add references). Add criteria for how amplification is defined. | |
| Chr # | Gain / Loss / Amp / LOH | Minimal Region Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build] | Minimal Region Cytoband | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Loss | 6q21-25[1][2] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | This locus harbours multiple candidate tumour suppressor genes including ATG5, AIM1, PRDM1, PTPRK, HACE1, and FOXO3[3][4][5]. |
Other less common chromosomal alterations include gain of 1p, 2q, 6p, 10q, 11q, 12q, 13q, 17q, 19p, 20q, and Xp; and loss of 1p36, 2p16, 4q12, 4q31-32, 5p14, 5q34-35, 6q13-14, 6q16-27, 11q22-23, 12q, 13q12-14, 13q14-34, 17p13, and entire chromosome X[6][7][8][9][10].
Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns
| Chromosomal Pattern | Molecular Pathogenesis | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE:
Co-deletion of 1p and 18q |
EXAMPLE: See chromosomal rearrangements table as this pattern is due to an unbalanced derivative translocation associated with oligodendroglioma (add reference). | EXAMPLE: Common (Oligodendroglioma) | EXAMPLE: D, P | ||
| EXAMPLE:
Microsatellite instability - hypermutated |
EXAMPLE: Common (Endometrial carcinoma) | EXAMPLE: P, T | |||
| Chromosomal Pattern | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isochromosome 6p[11] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | N/A |
| Isochromosome 7q[12] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | N/A |
Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)
| Gene | Genetic Alteration | Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE:EGFR
|
EXAMPLE: Exon 18-21 activating mutations | EXAMPLE: Oncogene | EXAMPLE: Common (lung cancer) | EXAMPLE: T | EXAMPLE: Yes (NCCN) | EXAMPLE: Exons 18, 19, and 21 mutations are targetable for therapy. Exon 20 T790M variants cause resistance to first generation TKI therapy and are targetable by second and third generation TKIs (add references). |
| EXAMPLE: TP53; Variable LOF mutations
|
EXAMPLE: Variable LOF mutations | EXAMPLE: Tumor Supressor Gene | EXAMPLE: Common (breast cancer) | EXAMPLE: P | EXAMPLE: >90% are somatic; rare germline alterations associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (add reference). Denotes a poor prognosis in breast cancer. | |
| EXAMPLE: BRAF; Activating mutations | EXAMPLE: Activating mutations | EXAMPLE: Oncogene | EXAMPLE: Common (melanoma) | EXAMPLE: T | ||
| Gene; Genetic Alteration | Presumed Mechanism (Tumor Suppressor Gene [TSG] / Oncogene / Other) | Prevalence (COSMIC / TCGA / Other) | Concomitant Mutations | Mutually Exclusive Mutations | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAK3[13][14] | Oncogene | 35.4%[13] | Unknown | Unknown | Pan-JAK and selective JAK3 inhibitors have been suggested as potential therapeutic options[13][15]. Clinical trials evaluating JAK inhibitors are in progress. | |||
| STAT3[16][17][18] | Oncogene | 6-26%[17][18] | Unknown | Unknown | STAT3 inhibitor may have potential therapeutic benefit in patients with STAT3 activating mutation[19]. | |||
| STAT5B[16][17] | Oncogene | 6%[17] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| PTPRK[5] | Other (acts on JAK/STAT pathway; underexpression leads to STAT3 activation[5]) | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| MYC[20] | Oncogene | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| PDGFRA[21] | Oncogene | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| EZH2[22] | Oncogene | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| RAS/KRAS/HRAS | Oncogene | <5%[23][24] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| FAS | Oncogene | 50-60%[25][26] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| KIT | Oncogene | 5-71% (China) | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| CTNNB1 | Oncogene | 16-30%[23][28] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| DDX3X[16] | Epigenetic modifier (RNA helicase) | 20%[16] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| KMT2D (MLL2)[16] | Epigenetic modifier | 38.2%[18] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| ARID1A[16] | Epigenetic modifier | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| EP300[16] | Epigenetic modifier | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| ASXL3[16] | Epigenetic modifier | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| BCOR[18] | Epigenetic modifier | 38.2%[18] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| TP53[16] | Tumor suppressor gene | 24-62%[29][30] | Unknown | Yes, associated with advanced stage disease[29]. | Unknown | |||
| RUNX3[31] | Tumor suppressor gene | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| MGA[16] | Tumor suppressor gene | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| PRDM1[32][4][33] | Tumor suppressor gene | Methylated in NK-92, KHYG-1, SNK-1, SNK-6 cell lines, 12/17 cases; Deleted in 8/18 cases; Mutated in NK-92 and KAI3 cell lines, 1/26 cases[32] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| ATG5[32] | Tumor suppressor gene | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | ||||
| AIM1[32] | Tumor suppressor gene | Methylated in NK-92, HANK1, NK-YS, SNK-1, YT cell lines; Mutated in in SNK-1 and SNK-6 cell lines[32] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| FOXO3[32][4] | Tumor suppressor gene | Mutated in 2/26 NKTCL and 1/9 ANKL[32] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |||
| HACE1[32][21] | Tumor suppressor gene | Mutated in 6/9 (67%) cell lines and 5/15 (33%) primary tumors[34] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in cBioportal (https://www.cbioportal.org/), COSMIC (https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic), ICGC (https://dcc.icgc.org/) and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content.
Epigenomic Alterations
A 2015 study by Lu, et al uncovered recurrent mutations in the RNA helicase gene DDX3X and other epigenetic modifiers including KMT2D (MLL2), ARID1A, EP300, and ASXL3[16].
Similarly, a 2015 study by Lee, et al reported that histone modification-related genes, including BCOR and KMT2D (MLL2), accounted for 38.2% of 34 ENKTL samples by next-generation sequencing[18].
Genes and Main Pathways Involved
Huang, et al described deregulation of several signaling pathways in NK T-cell lymphoma, main ones listed below[21]. A review by De Mel, et al, also outlines key molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of ENKTL[35].
| Gene; Genetic Alteration | Pathway | Pathophysiologic Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| JAK3, STAT3, and STAT5B; Activating mutations[21][35] | JAK/STAT pathway | Increased cell growth and proliferation |
| MYC, RUNX3[35] | MYC | Increased cell proliferation and survival |
| AKT and related genes[21] | AKT pathway | Increased cell growth, proliferation and survival |
| NF-κB related genes[21][35] | NF-κB pathway | Increased cell proliferation |
| PDGFRA[21][35] | PDGF pathway | Increased cell proliferation and survival |
| NOTCH1[35] | NOTCH1 pathway | Increased cell proliferation |
| AURKA[35] | Aurora kinase pathway[20] | Increased cell proliferation and cell cycle dysregulation |
Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods
- Select cases may require TCR gene rearrangement studies; otherwise, not routinely performed.
- EBV PCR testing may be used for disease monitoring
Familial Forms
N/A
Additional Information
This disease is defined/characterized as detailed below:
- Lymphoma of NK or T-cell lineage strongly associated with Epstein-Barr virus[36]. The lineage (NK or T-cell) has no clinical significance[37].
- Divided into nasal and non-nasal types, the latter most often occurring in the skin and intestinal tract[38][36].
- It is a destructive angiocentric disease characterized by vascular destruction and necrosis[39].
- Differential diagnosis: sinonasal carcinomas and other lymphomas of the nasal cavity, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[40].
The epidemiology/prevalence of this disease is detailed below:
- Most prevalent in East Asia and Latin America.
- Represents less than 1% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas in the United States
- Highest incidence among Asian Pacific Islanders and Hispanic populations[41].
The clinical features of this disease are detailed below:
Signs and symptoms - Nasal mass, nasal obstruction, nasal bleeding; Hoarseness, dysphagia, halitosis, airway obstruction, dysphonia; Abdominal pain, GI bleeding, bowel perforation[42]; B symptoms (fever, weight loss, night sweats) associated with higher clinical stage[43]
Laboratory findings - No specific findings; Cytopenias
The sites of involvement of this disease are detailed below:
- Most are nasal type involving the upper aerodigestive tract
- Extranasal type may involve skin, testis, and gastrointestinal tract[42].
- Bone marrow involvement is uncommon[44].
The morphologic features of this disease are detailed below:
- Diffuse infiltrate composed of admixture of small, medium, or large and anaplastic cells.
- Cells have irregularly folded nuclei and moderate pale cytoplasm.
- Loss of mucosal glands.
- Angiocentric and angiodestructive growth pattern with coagulative necrosis.
- Usually see apoptotic cells and mitotic figures
The pitfalls can include:
- Mucosal ulceration and superimposed inflammation can mimic an inflammatory process, particularly in less aggressive cases[45].
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the overlying mucosal epithelium can mimic squamous cell carcinoma[46][47].
The immunophenotype of this disease is detailed below:
Positive (universal) - EBER / EBV
Positive (majority) - cytoplasmic CD3ε, CD2, CD56, granzyme B, and TIA-1
Positive (subset) - TCR αβ/γδ, HLA-DR, CD25, pSTAT3, CXCL13, IRF4/MUM1, CD16, Fas, FasL, MATK, CD30[48][49][50][51][52][53][54]
Negative (universal) - CD4, CD8
Negative (subset) - Surface CD3 (subset of T-cell lineage)[42]
Links
5th edition World Health Organization (WHO) classification system
References
- ↑ Wong, K. F.; et al. (1997-09). "Identification of del(6)(q21q25) as a recurring chromosomal abnormality in putative NK cell lymphoma/leukaemia". British Journal of Haematology. 98 (4): 922–926. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.3223139.x. ISSN 0007-1048. PMID 9326190. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Ohshima, Koichi; et al. (2002-02). "Analysis of chromosome 6q deletion in EBV-associated NK cell leukaemia/lymphoma". Leukemia & Lymphoma. 43 (2): 293–300. doi:10.1080/10428190290006062. ISSN 1042-8194. PMID 11999560. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Iqbal, J.; et al. (2009-06). "Genomic analyses reveal global functional alterations that promote tumor growth and novel tumor suppressor genes in natural killer-cell malignancies". Leukemia. 23 (6): 1139–1151. doi:10.1038/leu.2009.3. ISSN 1476-5551. PMID 19194464. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 Karube, Kennosuke; et al. (2011-09-22). "Identification of FOXO3 and PRDM1 as tumor-suppressor gene candidates in NK-cell neoplasms by genomic and functional analyses". Blood. 118 (12): 3195–3204. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-346890. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 21690554.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 Chen, Yun-Wen; et al. (2015-03-05). "Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase κ directly targets STAT3 activation for tumor suppression in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma". Blood. 125 (10): 1589–1600. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-07-588970. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 25612622.
- ↑ Nakashima, Yasuhiro; et al. (2005-11). "Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia: different genomic alteration patterns of aggressive NK-cell leukemia and extranodal Nk/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type". Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer. 44 (3): 247–255. doi:10.1002/gcc.20245. ISSN 1045-2257. PMID 16049916. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Siu, L. L.; et al. (2000-12). "Consistent patterns of allelic loss in natural killer cell lymphoma". The American Journal of Pathology. 157 (6): 1803–1809. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64818-3. ISSN 0002-9440. PMC 1885756. PMID 11106552. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Siu, L. L.; et al. (1999-11). "Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia. Recognition of consistent patterns of genetic alterations". The American Journal of Pathology. 155 (5): 1419–1425. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65454-5. ISSN 0002-9440. PMC 1866965. PMID 10550295. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Wong, K. F.; et al. (1999-07). "Cytogenetic abnormalities in natural killer cell lymphoma/leukaemia--is there a consistent pattern?". Leukemia & Lymphoma. 34 (3–4): 241–250. doi:10.3109/10428199909050949. ISSN 1042-8194. PMID 10439361. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Ko, Y. H.; et al. (2001-04-15). "Comparative genomic hybridization study of nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma". Cytometry. 46 (2): 85–91. doi:10.1002/cyto.1069. ISSN 0196-4763. PMID 11309817.
- ↑ Tien, H. F.; et al. (1997-06). "Clonal chromosomal abnormalities as direct evidence for clonality in nasal T/natural killer cell lymphomas". British Journal of Haematology. 97 (3): 621–625. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.752711.x. ISSN 0007-1048. PMID 9207410. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Feldman, Andrew L.; et al. (2008-08). "Incidence of TCR and TCL1 gene translocations and isochromosome 7q in peripheral T-cell lymphomas using fluorescence in situ hybridization". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 130 (2): 178–185. doi:10.1309/PNXUKA1CFJMVGCN1. ISSN 0002-9173. PMC 3625137. PMID 18628085. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 13.0 13.1 13.2 Koo, Ghee Chong; et al. (2012-07). "Janus kinase 3-activating mutations identified in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma". Cancer Discovery. 2 (7): 591–597. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0028. ISSN 2159-8290. PMID 22705984. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Bouchekioua, A.; et al. (2014-02). "JAK3 deregulation by activating mutations confers invasive growth advantage in extranodal nasal-type natural killer cell lymphoma". Leukemia. 28 (2): 338–348. doi:10.1038/leu.2013.157. ISSN 1476-5551. PMID 23689514. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Nairismägi, M.-L.; et al. (2018-05). "Oncogenic activation of JAK3-STAT signaling confers clinical sensitivity to PRN371, a novel selective and potent JAK3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma". Leukemia. 32 (5): 1147–1156. doi:10.1038/s41375-017-0004-x. ISSN 1476-5551. PMC 5940653. PMID 29434279. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 16.00 16.01 16.02 16.03 16.04 16.05 16.06 16.07 16.08 16.09 16.10 Jiang, Lu; et al. (2015-09). "Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma". Nature Genetics. 47 (9): 1061–1066. doi:10.1038/ng.3358. ISSN 1546-1718. PMID 26192917. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 Küçük, Can; et al. (2015-01-14). "Activating mutations of STAT5B and STAT3 in lymphomas derived from γδ-T or NK cells". Nature Communications. 6: 6025. doi:10.1038/ncomms7025. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7743911 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 25586472. - ↑ Jump up to: 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 Lee, Seungbok; et al. (2015-07-10). "Genetic alterations of JAK/STAT cascade and histone modification in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type". Oncotarget. 6 (19): 17764–17776. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3776. ISSN 1949-2553. PMC 4627344. PMID 25980440.
- ↑ Wang, Yali; et al. (2023-08). "Preclinical characterization of WB737, a potent and selective STAT3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma". MedComm. 4 (4): e284. doi:10.1002/mco2.284. ISSN 2688-2663. PMC PMC10274570 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 37334274 Check|pmid=value (help). Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ↑ Jump up to: 20.0 20.1 Ng, Siok-Bian; et al. (2011-03). "Activated oncogenic pathways and therapeutic targets in extranodal nasal-type NK/T cell lymphoma revealed by gene expression profiling". The Journal of Pathology. 223 (4): 496–510. doi:10.1002/path.2823. ISSN 1096-9896. PMID 21294123. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 21.5 21.6 Huang, Yenlin; et al. (2010-02-11). "Gene expression profiling identifies emerging oncogenic pathways operating in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type". Blood. 115 (6): 1226–1237. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-221275. ISSN 1528-0020. PMC 2826234. PMID 19965620.
- ↑ Yan, Junli; et al. (2016-08-18). "EZH2 phosphorylation by JAK3 mediates a switch to noncanonical function in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma". Blood. 128 (7): 948–958. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-690701. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 27297789.
- ↑ Jump up to: 23.0 23.1 23.2 Hoshida, Yoshihiko; et al. (2003-03). "Analysis of p53, K-ras, c-kit, and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T cell lymphoma in northeast district of China". Cancer Science. 94 (3): 297–301. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01436.x. ISSN 1347-9032. PMC PMC11160272 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 12824925. Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ↑ Takahara, Miki; et al. (2004-01). "P53, N- and K-Ras, and beta-catenin gene mutations and prognostic factors in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma from Hokkaido, Japan". Human Pathology. 35 (1): 86–95. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2003.08.025. ISSN 0046-8177. PMID 14745729. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Shen, Lijun; et al. (2002-12). "Frequent deletion of Fas gene sequences encoding death and transmembrane domains in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma". The American Journal of Pathology. 161 (6): 2123–2131. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64490-2. ISSN 0002-9440. PMC 1850920. PMID 12466128. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Takakuwa, Tetsuya; et al. (2002-07-11). "Frequent mutations of Fas gene in nasal NK/T cell lymphoma". Oncogene. 21 (30): 4702–4705. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205571. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 12096347.
- ↑ Hongyo, T.; et al. (2000-05-01). "Specific c-kit mutations in sinonasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma in China and Japan". Cancer Research. 60 (9): 2345–2347. ISSN 0008-5472. PMID 10811105.
- ↑ Sugimoto, Kei-ji; et al. (2002-11). "Molecular analysis of oncogenes, ras family genes (N-ras, K-ras, H-ras), myc family genes (c-myc, N-myc) and mdm2 in natural killer cell neoplasms". Japanese Journal of Cancer Research: Gann. 93 (11): 1270–1277. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01234.x. ISSN 0910-5050. PMC 5926889. PMID 12460470. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 29.0 29.1 Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; et al. (2001-12). "p53 Mutations in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma from Mexico: association with large cell morphology and advanced disease". The American Journal of Pathology. 159 (6): 2095–2105. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63061-1. ISSN 0002-9440. PMC 1850589. PMID 11733360. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Hongyo, Tadashi; et al. (2005-02). "p53, K-ras, c-kit and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T-cell lymphoma in Korea and Japan". Oncology Reports. 13 (2): 265–271. ISSN 1021-335X. PMID 15643509. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Selvarajan, V.; et al. (2017-10). "RUNX3 is oncogenic in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and is transcriptionally regulated by MYC". Leukemia. 31 (10): 2219–2227. doi:10.1038/leu.2017.40. ISSN 1476-5551. PMC 5629367. PMID 28119527. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 32.4 32.5 32.6 32.7 Huang, Yenlin; et al. (2013-03). "Molecular underpinning of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology. 26 (1): 57–74. doi:10.1016/j.beha.2013.04.006. ISSN 1532-1924. PMID 23768641. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Küçük, Can; et al. (2011-12-13). "PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in natural killer cell malignancies". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (50): 20119–20124. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115128108. ISSN 1091-6490. PMC 3250125. PMID 22143801.
- ↑ Küçük, Can; et al. (2013-01). "HACE1 is a tumor suppressor gene candidate in natural killer cell neoplasms". The American Journal of Pathology. 182 (1): 49–55. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.09.012. ISSN 1525-2191. PMC 3532710. PMID 23142381. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 35.5 35.6 de Mel, Sanjay; et al. (2019-04-02). "Molecular pathogenic pathways in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma". Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 12 (1): 33. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0716-7. ISSN 1756-8722. PMC 6444858. PMID 30935402.
- ↑ Jump up to: 36.0 36.1 Jaffe, E. S.; et al. (1999-01). "Extranodal peripheral T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 111 (1 Suppl 1): S46–55. ISSN 0002-9173. PMID 9894469. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Wang, Hua; et al. (2021-09). "NK-/T-cell lymphomas". Leukemia. 35 (9): 2460–2468. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01313-2. ISSN 1476-5551. PMC 8410593 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 34117356 Check|pmid=value (help). Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Chan J. K. C., et al., (2017). Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, in World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised 4th edition. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Arber DA, Hasserjian RP, Le Beau MM, Orazi A, and Siebert R, Editors. Revised 4th Edition. IARC Press: Lyon, France, p.368-371.
- ↑ Aviles, A.; et al. (1992). "Angiocentric T-cell lymphoma of the nose, paranasal sinuses and hard palate". Hematological Oncology. 10 (3–4): 141–147. doi:10.1002/hon.2900100303. ISSN 0278-0232. PMID 1398510.
- ↑ Steele, Toby O.; et al. (2016-09). "Lymphoma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: A case series". American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy. 30 (5): 335–339. doi:10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4347. ISSN 1945-8932. PMID 27657899. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Haverkos, Bradley M.; et al. (2016-12). "Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL-NT): An update on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and natural history in North American and European cases". Current hematologic malignancy reports. 11 (6): 514–527. doi:10.1007/s11899-016-0355-9. ISSN 1558-8211. PMC 5199232. PMID 27778143. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jump up to: 42.0 42.1 42.2 Thida AM, Gohari P. Extranodal NK-Cell Lymphoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559207/
- ↑ Takahara, Miki; et al. (2021-06-25). "Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein-Barr Virus Relation". Microorganisms. 9 (7): 1381. doi:10.3390/microorganisms9071381. ISSN 2076-2607. PMC 8304202 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 34202088 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Wong, K. F.; et al. (2001-02). "Bone marrow involvement by nasal NK cell lymphoma at diagnosis is uncommon". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 115 (2): 266–270. doi:10.1309/E5PR-6A9R-Q02N-8QVW. ISSN 0002-9173. PMID 11211616. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Devins, K., Schuster, S.J., Caponetti, G.C. et al. Rare case of low-grade extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, arising in the setting of chronic rhinosinusitis and harboring a novel N-terminal KIT mutation. Diagn Pathol 13, 92 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-018-0765-1
- ↑ Ling, Yi-Hong; et al. (2015-09). "Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia mimicking invasive squamous cell carcinoma in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a report of 34 cases". Histopathology. 67 (3): 404–409. doi:10.1111/his.12656. ISSN 1365-2559. PMID 25619876. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Xiang, Chun-Xiang; et al. (2019-07). "Laryngeal Extranodal Nasal-type Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 31 Cases in China". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 43 (7): 995–1004. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000001266. ISSN 1532-0979. PMID 31045893. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Li, Shaoying; et al. (2013-01). "Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a report of 73 cases at MD Anderson Cancer Center". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 37 (1): 14–23. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31826731b5. ISSN 1532-0979. PMID 23232851. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jhuang, Jie-Yang; et al. (2015-02). "Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type in Taiwan: a relatively higher frequency of T-cell lineage and poor survival for extranasal tumors". Human Pathology. 46 (2): 313–321. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2014.11.008. ISSN 1532-8392. PMID 25554090. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Pongpruttipan, Tawatchai; et al. (2012-04). "Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, includes cases of natural killer cell and αβ, γδ, and αβ/γδ T-cell origin: a comprehensive clinicopathologic and phenotypic study". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 36 (4): 481–499. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824433d8. ISSN 1532-0979. PMID 22314189. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Jaffe, E. S.; et al. (1996-01). "Report of the Workshop on Nasal and Related Extranodal Angiocentric T/Natural Killer Cell Lymphomas. Definitions, differential diagnosis, and epidemiology". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 20 (1): 103–111. doi:10.1097/00000478-199601000-00012. ISSN 0147-5185. PMID 8540601. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Ohshima, K.; et al. (1997-11). "Nasal T/NK cell lymphomas commonly express perforin and Fas ligand: important mediators of tissue damage". Histopathology. 31 (5): 444–450. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2559.1997.2880887.x. ISSN 0309-0167. PMID 9416485. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Takata, Katsuyoshi; et al. (2015-01). "Primary cutaneous NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type and CD56-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a cellular lineage and clinicopathologic study of 60 patients from Asia". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 39 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000312. ISSN 1532-0979. PMID 25188863. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Kuo, Tseng-Tong; et al. (2004-10). "Nasal NK/T cell lymphoma in Taiwan: a clinicopathologic study of 22 cases, with analysis of histologic subtypes, Epstein-Barr virus LMP-1 gene association, and treatment modalities". International Journal of Surgical Pathology. 12 (4): 375–387. doi:10.1177/106689690401200410. ISSN 1066-8969. PMID 15494863. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
Notes
*Primary authors will typically be those that initially create and complete the content of a page. If a subsequent user modifies the content and feels the effort put forth is of high enough significance to warrant listing in the authorship section, please contact the Associate Editor or other CCGA representative. When pages have a major update, the new author will be acknowledged at the beginning of the page, and those who contributed previously will be acknowledged below as a prior author.
Prior Author(s):
*Citation of this Page: “Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated 03/24/2025, https://ccga.io/index.php/HAEM5:Extranodal_NK/T-cell_lymphoma.