Difference between revisions of "BRST5:Secretory carcinoma"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
Kgeiersbach (talk | contribs) |
Kgeiersbach (talk | contribs) (added gene fusion diagram) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Secretory carcinoma}} | |
| + | |||
| + | [[BRST5:Table_of_Contents|Breast Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | ||
==Primary Author(s)*== | ==Primary Author(s)*== | ||
Hui Chen, MD, PhD, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA | Hui Chen, MD, PhD, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
Katherine Geiersbach, MD, Mayo Clinic - Rochester, MN, USA | Katherine Geiersbach, MD, Mayo Clinic - Rochester, MN, USA | ||
==WHO Classification of Disease== | ==WHO Classification of Disease== | ||
| − | + | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Structure | !Structure | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Book | |Book | ||
| − | | | + | |Breast Tumours (5th ed.) |
|- | |- | ||
|Category | |Category | ||
| − | | | + | |Epithelial tumours of the breast |
|- | |- | ||
|Family | |Family | ||
| − | | | + | |Rare and salivary gland-type tumours: Introduction |
|- | |- | ||
|Type | |Type | ||
| − | | | + | |Secretory carcinoma |
|- | |- | ||
|Subtype(s) | |Subtype(s) | ||
| − | | | + | |N/A |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
==WHO Essential and Desirable Genetic Diagnostic Criteria== | ==WHO Essential and Desirable Genetic Diagnostic Criteria== | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|WHO Desirable Criteria (Genetics)* | |WHO Desirable Criteria (Genetics)* | ||
| − | | | + | |''ETV6''::''NTRK3'' fusion |
|- | |- | ||
|Other Classification | |Other Classification | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
<nowiki>*</nowiki>Note: These are only the genetic/genomic criteria. Additional diagnostic criteria can be found in the [https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/home <u>WHO Classification of Tumours</u>]. | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Note: These are only the genetic/genomic criteria. Additional diagnostic criteria can be found in the [https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/home <u>WHO Classification of Tumours</u>]. | ||
==Related Terminology== | ==Related Terminology== | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
==Gene Rearrangements== | ==Gene Rearrangements== | ||
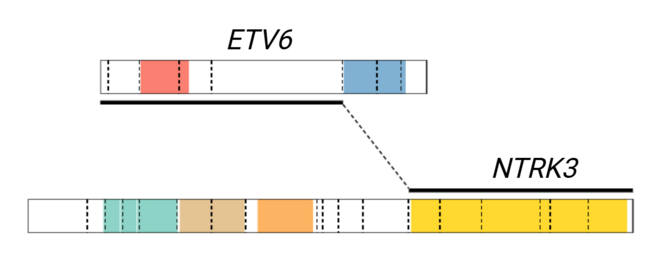
| − | + | [[File:ETV6-NTRK3 fusion diagram.tif|left|frameless|655x655px|Gene fusion diagram showing the canonical breakpoints in exon 5 of ''ETV6'' (NM_001987) and exon 15 of ''NTRK3'' (NM_001012338). Alternate fusion breakpoints include exon 4 of ''ETV6'' and exon 14 of ''NTRK3''.]] | |
| + | <br /> | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 67: | Line 69: | ||
|D, P, T | |D, P, T | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |The ''ETV6''::''NTRK3'' fusion is diagnostic of secretory carcinoma in the appropriate morphologic and clinical context.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Arce|first=C.|last2=Cortes-Padilla|first2=D.|last3=Huntsman|first3=D. G.|last4=Miller|first4=M. A.|last5=Dueñnas-Gonzalez|first5=A.|last6=Alvarado|first6=A.|last7=Pérez|first7=V.|last8=Gallardo-Rincón|first8=D.|last9=Lara-Medina|first9=F.|date=2005-06-17|title=Secretory carcinoma of the breast containing the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene in a male: case report and review of the literature|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15963235|journal=World Journal of Surgical Oncology|volume=3|pages=35|doi=10.1186/1477-7819-3-35|issn=1477-7819|pmc=1184104|pmid=15963235}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Jacob|first=John Doromal|last2=Hodge|first2=Caitlin|last3=Franko|first3=Jan|last4=Pezzi|first4=Christopher M.|last5=Goldman|first5=Charles D.|last6=Klimberg|first6=Vicki Suzanne|date=2016-06|title=Rare breast cancer: 246 invasive secretory carcinomas from the National Cancer Data Base|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27040042|journal=Journal of Surgical Oncology|volume=113|issue=7|pages=721–725|doi=10.1002/jso.24241|issn=1096-9098|pmid=27040042}}</ref> This fusion is responsive to TRK inhibitor therapies such as larotrectinib abd entrectinib. | + | |The ''ETV6''::''NTRK3'' fusion is diagnostic of secretory carcinoma in the appropriate morphologic and clinical context.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Arce|first=C.|last2=Cortes-Padilla|first2=D.|last3=Huntsman|first3=D. G.|last4=Miller|first4=M. A.|last5=Dueñnas-Gonzalez|first5=A.|last6=Alvarado|first6=A.|last7=Pérez|first7=V.|last8=Gallardo-Rincón|first8=D.|last9=Lara-Medina|first9=F.|date=2005-06-17|title=Secretory carcinoma of the breast containing the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene in a male: case report and review of the literature|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15963235|journal=World Journal of Surgical Oncology|volume=3|pages=35|doi=10.1186/1477-7819-3-35|issn=1477-7819|pmc=1184104|pmid=15963235}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Jacob|first=John Doromal|last2=Hodge|first2=Caitlin|last3=Franko|first3=Jan|last4=Pezzi|first4=Christopher M.|last5=Goldman|first5=Charles D.|last6=Klimberg|first6=Vicki Suzanne|date=2016-06|title=Rare breast cancer: 246 invasive secretory carcinomas from the National Cancer Data Base|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27040042|journal=Journal of Surgical Oncology|volume=113|issue=7|pages=721–725|doi=10.1002/jso.24241|issn=1096-9098|pmid=27040042}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Li|first=Dali|last2=Xiao|first2=Xiuying|last3=Yang|first3=Wentao|last4=Shui|first4=Ruohong|last5=Tu|first5=Xiaoyu|last6=Lu|first6=Hongfen|last7=Shi|first7=Daren|date=2012-04|title=Secretory breast carcinoma: a clinicopathological and immunophenotypic study of 15 cases with a review of the literature|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22157932|journal=Modern Pathology: An Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc|volume=25|issue=4|pages=567–575|doi=10.1038/modpathol.2011.190|issn=1530-0285|pmid=22157932}}</ref> This fusion is responsive to TRK inhibitor therapies such as larotrectinib abd entrectinib. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 78: | Line 80: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== | ==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 99: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns== | ==Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 114: | Line 120: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)== | + | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL) == | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 132: | Line 139: | ||
| | | | ||
|}Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in [https://www.cbioportal.org/ <u>cBioportal</u>], [https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic <u>COSMIC</u>], and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content. | |}Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in [https://www.cbioportal.org/ <u>cBioportal</u>], [https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic <u>COSMIC</u>], and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Epigenomic Alterations== | ==Epigenomic Alterations== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 148: | Line 157: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods== | ==Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods== | ||
FISH, RT-PCR, next generation sequencing | FISH, RT-PCR, next generation sequencing | ||
| Line 158: | Line 169: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | ==Notes== | + | ==Notes== |
| − | |||
| − | Prior Author(s): | + | Prior Author(s): |
| − | ==References== | + | ==References == |
| − | + | <references /> | |
| − | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki>''Citation of this Page'': “Secretory carcinoma”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated {{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}}, <nowiki>https://ccga.io/index.php/BRST5:Secretory carcinoma</nowiki>. | |
| − | + | [[Category:BRST5]] | |
| + | [[Category:DISEASE]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Diseases S]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:32, 16 April 2025
Breast Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)
Primary Author(s)*
Hui Chen, MD, PhD, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA
Katherine Geiersbach, MD, Mayo Clinic - Rochester, MN, USA
WHO Classification of Disease
| Structure | Disease |
|---|---|
| Book | Breast Tumours (5th ed.) |
| Category | Epithelial tumours of the breast |
| Family | Rare and salivary gland-type tumours: Introduction |
| Type | Secretory carcinoma |
| Subtype(s) | N/A |
WHO Essential and Desirable Genetic Diagnostic Criteria
| WHO Essential Criteria (Genetics)* | |
| WHO Desirable Criteria (Genetics)* | ETV6::NTRK3 fusion |
| Other Classification |
*Note: These are only the genetic/genomic criteria. Additional diagnostic criteria can be found in the WHO Classification of Tumours.
Related Terminology
| Acceptable | |
| Not Recommended |
Gene Rearrangements
| Driver Gene | Fusion(s) and Common Partner Genes | Molecular Pathogenesis | Typical Chromosomal Alteration(s) | Prevalence -Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTRK3 | ETV6::NTRK3[1] | Fusion results in constitutive activation of NTRK3 tyrosine kinase | t(12;15)(p13;q25) | Common | D, P, T | The ETV6::NTRK3 fusion is diagnostic of secretory carcinoma in the appropriate morphologic and clinical context.[2][3][4] This fusion is responsive to TRK inhibitor therapies such as larotrectinib abd entrectinib. | |
Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH
| Chr # | Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH | Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size] | Relevant Gene(s) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns
| Chromosomal Pattern | Molecular Pathogenesis | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)
| Gene | Genetic Alteration | Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in cBioportal, COSMIC, and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content.
Epigenomic Alterations
Genes and Main Pathways Involved
| Gene; Genetic Alteration | Pathway | Pathophysiologic Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| NTRK3; Activating fusion with 5' partner ETV6 | MAPK/PI3K/AKT signaling | Increased cell growth and proliferation |
Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods
FISH, RT-PCR, next generation sequencing
Familial Forms
None
Additional Information
Links
https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantjuvenile.html
Notes
Prior Author(s):
References
- ↑ Tognon, Cristina; et al. (2002-11). "Expression of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion as a primary event in human secretory breast carcinoma". Cancer Cell. 2 (5): 367–376. doi:10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00180-0. ISSN 1535-6108. PMID 12450792. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Arce, C.; et al. (2005-06-17). "Secretory carcinoma of the breast containing the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene in a male: case report and review of the literature". World Journal of Surgical Oncology. 3: 35. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-3-35. ISSN 1477-7819. PMC 1184104. PMID 15963235.
- ↑ Jacob, John Doromal; et al. (2016-06). "Rare breast cancer: 246 invasive secretory carcinomas from the National Cancer Data Base". Journal of Surgical Oncology. 113 (7): 721–725. doi:10.1002/jso.24241. ISSN 1096-9098. PMID 27040042. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Li, Dali; et al. (2012-04). "Secretory breast carcinoma: a clinicopathological and immunophenotypic study of 15 cases with a review of the literature". Modern Pathology: An Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. 25 (4): 567–575. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.190. ISSN 1530-0285. PMID 22157932. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
*Citation of this Page: “Secretory carcinoma”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated 04/16/2025, https://ccga.io/index.php/BRST5:Secretory carcinoma.